A stepper motor rotates with a fixed step angle, just like the second hand of a clock. Highly accurate positioning can be performed with open-loop control thanks to the mechanical structure within the motor.
Accurate Positioning (Number of Steps)
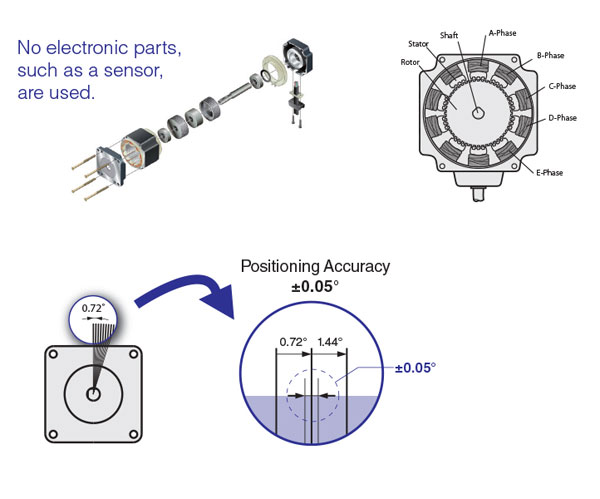
While having full control of rotation and speed, the simple structure of stepper motors is achieved without using electrical components, such as an encoder within the motor. For this reason, stepper motors are very robust and have high reliability with very few failures. As for stopping accuracy, ±0.05° (without cumulative pitch errors) is very accurate. Because positioning of stepper motors is performed by open-loop control and operated by the magnetized stator and magnetic rotor with small teeth, stepper motors have a higher follow-up mechanism toward commands than that of servo motors. Also, no hunting occurs when stopping stepper motors. They are also excellent in belt drives, which have low rigidity.
Useful for Speed Control and Position Control
When pulses are input to a driver through a pulse generator, stepper motors position according to the number of input pulses. The basic step angle of 5-phase stepper motors is 0.72° and 1.8° stepper motor for 2-phase motors. The rotating speed of the stepper motor is determined by the speed of the pulse frequency (Hz) given to the driver, and it is possible to freely change the motor rotation by simply changing the number of input pulses or frequencies to the driver. Stepper motors not only serve as position control motors, but also as speed control motors with high synchronization.
Stepper Motors Uses:
• High frequency, repetitive positioning of fixed step angles
• Positioning that requires long stopping time due to width adjustment, etc.
• Fluctuating loads and changing rigidity
• Positioning that divides 1 cycle
• Motor shafts that requires synchronous operation
See more:https://www.oyostepper.com/
Aucun commentaire:
Publier un commentaire